Server Installation
Prerequisite
Before installing Plant-it, make sure you have the following prerequisites:
dockerversion 3 or abovedocker-compose
Quickstart
Installing Plant-it is pretty straight forward, in order to do so follow these steps:
- Create a folder where you want to place all Plant-it related files.
-
Inside that folder, create a file named
docker-compose.ymlwith this content:name: plant-it services: server: image: msdeluise/plant-it-server:latest env_file: server.env depends_on: - db - cache restart: unless-stopped volumes: - "./upload-dir:/upload-dir" - "./certs:/certificates" ports: - "8080:8080" - "3000:3000" db: image: mysql:8.0 restart: always env_file: server.env volumes: - "./db:/var/lib/mysql" cache: image: redis:7.2.1 restart: always -
Inside that folder, create a file named
server.envwith this content:# # DB # MYSQL_HOST=db MYSQL_PORT=3306 MYSQL_USERNAME=root MYSQL_PSW=root MYSQL_DATABASE=bootdb MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root # # JWT # JWT_SECRET=putTheSecretHere JWT_EXP=1 # # Server config # USERS_LIMIT=-1 UPLOAD_DIR=/upload-dir API_PORT=8080 TREFLE_KEY= LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG ALLOWED_ORIGINS=* # # Cache # CACHE_TTL=86400 CACHE_HOST=cache CACHE_PORT=6379 # # SSL # SSL_ENABLED=false CERTIFICATE_PATH=/certificates/ -
Run the docker compose file (
docker compose -f docker-compose.yml up -d), then the service will be available atlocalhost:3000, while the REST API will be available atlocalhost:8080/api(localhost:8080/api/swagger-ui/index.htmlfor the documentation of them).
Configuration
The server.env file is used to pass configurations to the server. An example of properties and descriptions is the following:
#
# DB
#
MYSQL_HOST=db
MYSQL_PORT=3306
MYSQL_USERNAME=root
MYSQL_PSW=root
MYSQL_DATABASE=bootdb
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root
#
# JWT
#
JWT_SECRET=putTheSecretHere
JWT_EXP=1
#
# Server config
#
USERS_LIMIT=-1 # less then 0 means no limit
UPLOAD_DIR=/upload-dir # path to the directory used to store uploaded images, if on docker deployment leave as it is and change the volume binding in the docker-compose file if needed
API_PORT=8080
TREFLE_KEY=
ALLOWED_ORIGINS=* # CORS allowed origins (comma separated list)
LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG # could be: DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR
UPDATE_EXISTING=false # update missing fields using Trefle service, useful on system version update if new fields are introduced
CONTACT_MAIL=foo@bar.com # address used as "contact" for template email
REMINDER_NOTIFY_CHECK=0 30 7 * * * # 6-values crontab expression to set the check time for reminders
MAX_REQUESTS_PER_MINUTE=100 # rate limiting of the upcoming requests
NTFY_ENABLED=true # if "false" ntfy service won't be available as notification dispatcher
#
# SSL
#
SSL_ENABLED=false
CERTIFICATE_PATH=/certificates/ # path to files to use for ssl. If on docker deployment leave as it is and change the volume binding in the docker-compose file if needed
#
# Cache
#
CACHE_TTL=86400
CACHE_HOST=cache
CACHE_PORT=6379
#
# SMTP
#
SMTP_HOST=
SMTP_PORT=
SMTP_EMAIL=
SMTP_PASSWORD=
SMTP_AUTH=
SMTP_START_TTL=
Change ports binding
Backend
If you don't want to use the default port 8080, you can do the following:
- change the port binding in the
docker-compose.ymlfile, e.g.9090:8080to setup the port9090for the backend service,
Frontend
If you don't want to use the default port 3000, you can do the following:
- change the port binding in the
docker-compose.ymlfile, e.g.4040:3000to setup the port4040for the frontend service
Complete example
Let's say that you want to run Plant-it on a server with IP http://192.168.1.103 and want to have:
- the backend on port
8089, - the frontend on port
3009.
Then this will be you configuration for the docker-compose.yml file:
name: plant-it
services:
server:
image: msdeluise/plant-it-server:latest
env_file: server.env
depends_on:
- db
- cache
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- "./upload-dir:/upload-dir"
- "./certs:/certificates"
ports:
- "8089:8080"
- "3009:3000"
db:
image: mysql:8.0
restart: always
env_file: server.env
volumes:
- "./db:/var/lib/mysql"
cache:
image: redis:7.2.1
restart: always
server.env file:
#
# DB
#
MYSQL_HOST=db
MYSQL_PORT=3306
MYSQL_USERNAME=root
MYSQL_PSW=root
MYSQL_DATABASE=bootdb
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root
#
# JWT
#
JWT_SECRET=32characterscomplicatedsecret
JWT_EXP=1
#
# Server config
#
USERS_LIMIT=2
UPLOAD_DIR=/upload-dir
API_PORT=8080
TREFLE_KEY=
ALLOWED_ORIGINS=*
#
# Cache
#
CACHE_TTL=86400
CACHE_HOST=cache
CACHE_PORT=6379
#
# SSL
#
SSL_ENABLED=false
CERTIFICATE_PATH=/certificates/
Example of traefik deployment
This is an example of deployment using traefik:
version: '3'
services:
reverse-proxy:
image: traefik:v3.0
command: --api.insecure=true --providers.docker
ports:
- "80:80"
- "8080:8080"
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
server:
image: msdeluise/plant-it-server:latest
env_file: server.env
depends_on:
- db
- cache
restart: unless-stopped
labels:
- "traefik.enable=true"
- "traefik.http.routers.app.rule=Host(`plant-it.docker.localhost`)"
- "traefik.http.routers.app.service=server"
- "traefik.http.routers.app.entrypoints=http"
- "traefik.http.services.server.loadbalancer.server.port=3000"
- "traefik.http.routers.api.rule=Host(`plant-it-api.docker.localhost`)"
- "traefik.http.routers.api.service=server-api"
- "traefik.http.routers.api.entrypoints=http"
- "traefik.http.services.server-api.loadbalancer.server.port=8080"
db:
image: mysql:8.0
restart: always
env_file: server.env
volumes:
- "./db:/var/lib/mysql"
labels:
- "traefik.enable=false"
cache:
image: redis:7.2.1
restart: always
labels:
- "traefik.enable=false"
Visit http://plant-it.docker.localhost for accessing the app, and http://plant-it-api.docker.localhost/api/swagger-ui/index.html for accessing the Swagger UI.
Use http://plant-it-api.docker.localhost as server URL when request in the app setup.
SMTP Configuration for Email Notifications
An SMTP server can be used to send notifications to users, such as password reset emails. To configure the usage of an SMTP server, the following properties need to be set in the server.env file:
- SMTP_HOST: The host of the SMTP server.
- SMTP_PORT: The port of the SMTP server.
- SMTP_EMAIL: The email address used to send notifications.
- SMTP_PASSWORD: The password of the email account used for authentication.
- SMTP_AUTH: This parameter enables or disables authentication for the SMTP server.
- SMTP_START_TLS: This parameter enables or disables the use of STARTTLS for secure communication with the SMTP server.
- CONTACT_MAIL: contact address to use in the email templates if a user want to contact the administrator
Email credentials
Please note that some providers, such as Gmail, may require the use of an application-specific password for authentication.
Example Gmail Configuration
SMTP_HOST=smtp.gmail.com
SMTP_PORT=587
SMTP_EMAIL=your-email@gmail.com
SMTP_PASSWORD=your-application-password
SMTP_AUTH=true
SMTP_START_TTL=true
CONTACT_MAIL=your-email@gmail.com
Enable SSL
Deprecation
Please be aware that SSL feature is deprecated. If you want to use SSL, you can use some application proxy like traefik or nginx.
To enable SSL for your Plant-it deployment, follow these steps:
- Set SSL Enabled Property: Ensure that SSL is enabled by adding the property
SSL_ENABLED=trueto theserver.envfile. - Create Volume Binding: Add a volume binding
"./certs:/certificates"to theserver.envservices in yourdocker-compose.ymlfile. This allows the services to access SSL certificates stored in the./certsdirectory.
Complete Example
Let's say that you want to run Plant-it on a server with IP https://192.168.1.103 and want to have:
- the backend on port
8089, - the frontend on port
3009.
docker-compose.yml:
name: plant-it
services:
server:
image: msdeluise/plant-it-server:latest
env_file: server.env
depends_on:
- db
- cache
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- "./upload-dir:/upload-dir"
- "certs:/certificates"
ports:
- "8089:8080"
- "3009:3000"
db:
image: mysql:8.0
restart: always
env_file: server.env
volumes:
- "./db:/var/lib/mysql"
cache:
image: redis:7.2.1
restart: always
server.env:
MYSQL_HOST=db
MYSQL_PORT=3306
MYSQL_USERNAME=root
MYSQL_PSW=root
MYSQL_DATABASE=bootdb
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root
JWT_SECRET=32characterscomplicatedsecret
JWT_EXP=1
USERS_LIMIT=2
UPLOAD_DIR=/upload-dir
API_PORT=8080
CACHE_TTL=86400
CACHE_HOST=cache
CACHE_PORT=6379
TREFLE_KEY=
ALLOWED_ORIGINS=*
SSL_ENABLED=true
CERTIFICATE_PATH=/certificates/
This setup creates a self-hosted certificate for both the backend and frontend services.
Accept certificates
In some cases, certain browsers may require explicit acceptance of certificates from both the frontend and backend of the application, even if they share the same certificate. This scenario typically arises when encountering a "Cannot connect to the backend" error message and SSL is enabled. To resolve this issue, users may need to navigate to both the frontend and backend URLs of the application and manually accept the certificate presented by each. By acknowledging the certificates, users can establish a trusted connection between their browser and the application's frontend and backend servers, thereby resolving connectivity issues.
Provide Custom Certificate
If you prefer to use your own certificate, simply place the app.key and app.crt files inside the CERTIFICATE_PATH folder.
Get the API Key
In order to get the API key, it's needed to use the REST API of the service:
- Open your browser and navigate to
http://<server-ip>:<server-port>/api/swagger-ui/index.html. - Obtain a JWT token by calling the
POST /authentication/loginendpoint with your credentials. - Set the JWT token in Swagger for the subsequent calls by using the "Authorize" button at the top.
- Create a new API key by calling the
POST /api-keyendpoint, optionally passing a name for the key.
Homepage dashboard integration
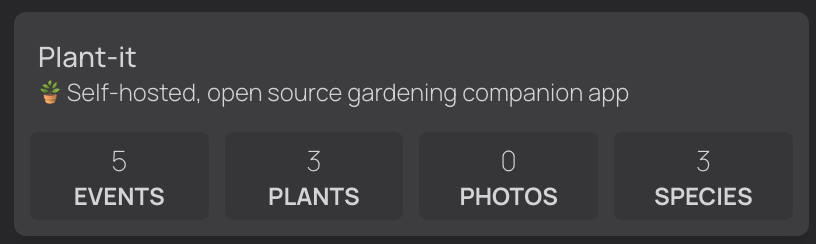
The project offers a widget for integrates the service with the popular dashboard called homepage. In order to use it, simply place the widget as above in the configuration yml file of the dashboard:
- Plant-it:
href: <server-app-url>
description: 🪴 Self-hosted, open source gardening companion app
widget:
type: plantit
url: <server-backend-url>
key: <you-key>
Kubernetes Deployment
This guide will help you deploy your project using Kubernetes with Minikube. Follow the steps below to set up and access your application.
Prerequisites
- Ensure you have Minikube installed and running.
- Ensure
kubectlis installed and configured to communicate with your Minikube cluster. - (if using Helm) Ensure Helm is installed.
Deployment Steps
Using kubectl
First, download the contents of the deployment/kubernetes directory from the project repository, then:
-
Run Minikube:
minikube start --driver=docker --mount --mount-string="/tmp/plant-it-data:/mnt/data" -
Deploy the DB Secrets:
kubectl apply -f secret.yml -
Deploy the DB ConfigMaps:
kubectl apply -f config.yml -
Deploy the Database:
kubectl apply -f db.yml -
Deploy the Cache:
kubectl apply -f cache.yml -
Deploy the Server:
kubectl apply -f server.yml
If you want to change the configuration values, edit the content of config.yml and secret.yml files.
Using Helm
First, download the contents of the deployment/helm directory from the project repository, then:
-
Run Minikube:
minikube start --driver=docker --mount --mount-string="/tmp/plant-it-data:/mnt/data" -
Create and Modify
my-values.ymlFile: Create a new file calledmy-values.ymlto override the default settings provided in thevalues.ymlfile. You can copy the content fromvalues.ymland modify it according to your configuration needs. This ensures your custom values are applied without altering the default configuration. -
Install the Helm Chart:
This command confirms that the values inhelm install plantit helm --values helm/values.yml -f helm/my-values.ymlhelm/values.ymlwill be used as the base configuration, and any values specified inhelm/my-values.ymlwill override the defaults.
Using TrueCharts
The Plant-it service is also available on TrueCharts, which simplifies the deployment process. You can find the chart for Plant-it here.
Please note that I am not the creator of these charts. For any issues or detailed instructions on how to deploy using TrueCharts, please refer to the official TrueCharts documentation.
Access the Application
Once the deployment is complete, you can access the application and its Swagger UI at the following URLs:
- Application:
http://<minikube_ip>:3000 - Swagger UI:
http://<minikube_ip>:8080/api/swagger-ui/index.html
Replace <minikube_ip> with the IP address returned by the following command:
minikube ip
⚠ Known Issue - Minikube IP not Accessible
If you encounter issues accessing the NodePort service using MinikubeIP:NodePort, execute the following command to expose the service and obtain a direct URL:
minikube service server-service
Then, open the printed links in your browser to access the application and Swagger UI.